GECOsistema has more than 15 years long scientific, technical and administrative experience in environmental and human health risk assessment (EHHRA) following national and international standards.
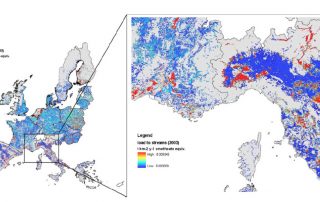
GECOsistema scientists have completed diverse EHHRAs in Italy, Europe and internationally. These assessments evaluated risk from contaminated sites, waste incinerators and landfills, airborne emissions, leachate, runoff, land application of sludges, liquid effluents and pesticides.
GECOsistema has a multidisciplinary team with specialization in toxicology, environmental engineering, biology, fate and transport modeling to support human health risk assessment.
Environmental and Human Health Risk Assessment Services includes:
- atmospheric emission, contaminated sites, landfills, waste and power plant (RBCA, USEPA HHRAP, OEHHA)
- Pesticides Risk Assessment (FOCUS)
- Chemical Risk Assessment (REACH)
We apply appropriate risk assessment tools and methodologies to support all phases of environmental decision making, including:
- Conceptual modelling to support human health risk assessment
- Identification of source-pathway-receptor linkages (potential pollutant linkages)
- Calculation of site-specific risk-based screening values and performing screening level risk assessments under applicable regulatory guidance
- Risk Analysis compliant to Italian and European Directive
- Modelling approaches including CLEA v1.04, RISC4, RBCA, RISC-HUMAN
- HHRAP Human Health Risk Assessment Protocol for Hazardous Waste Combustion Facilities
- Application of a toolbox of contaminant transport models (e.g., Multimed, MEPAS, HELP, RESRAD, MODFLOW, ArcInfo GRID, HSSM, USGS MOC) to support risk assessments
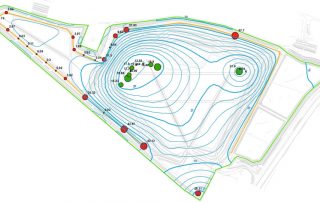
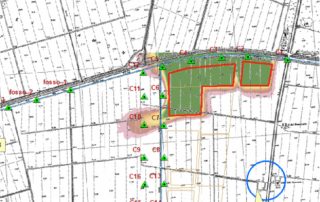
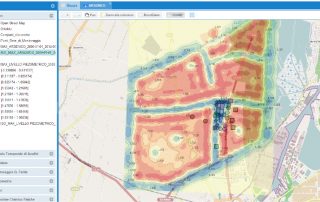
GECOsistema has developed RISK-GIS as ArcMap ESRI plug-in tool for the application of quantitative human health risk assessment from exposure to hazardous chemicals were released or present in multiple environmental media.
RISK-GIS allows an experienced user to proceed in several stages involving the human health risk quantification through the use of fate and transport models of the of pollutants in different environmental media (MODFLOW, MT3D, HSSM, Vleach, ISC3, Caline), characterization of the receptors exposed to and use of models USEPA (RBCA, HWIR, CALTOX,) for the estimation of exposure and risk.
RISK-GIS is suitable for both assessments of the risk to human health posed by contamination of air, soil and groundwater at industrial sites.
The purpose of the assessment is to ensure that decision makers consider the environmental impacts when deciding whether or not to proceed with a project. The International Association for Impact Assessment (IAIA) defines an environmental impact assessment as “the process of identifying, predicting, evaluating and mitigating the biophysical, social, and other relevant effects of development proposals prior to major decisions being taken and commitments made.”[1]
EIAs are unique in that they do not require adherence to a predetermined environmental outcome, but rather they require decision makers to account for environmental values in their decisions and to justify those decisions in light of detailed environmental studies and public comments on the potential environmental impacts.
Strategic environmental assessment (SEA) is a systematic decision support process, aiming to ensure that environmental and possibly other sustainability aspects are considered effectively in policy, plan and programme making. In this context, following Fischer (2007)[1] SEA may be seen as:
- a structured, rigorous, participative, open and transparent environmental impact assessment (EIA) based process, applied particularly to plans and programmes, prepared by public planning authorities and at times private bodies,
- a participative, open and transparent,possibly non-EIA-based process, applied in a more flexible manner to policies, prepared by public planning authorities and at times private bodies, or
- a flexible non-EIA based process,applied to legislative proposals and other policies, plans and programmes in political/cabinet decision-making.
Effective SEA works within a structured and tiered decision framework,aiming to support more effective and efficient decision-making for sustainable development and improved governance by providing for a substantive focus regarding questions, issues and alternatives to be considered in policy, plan and programme(PPP) making.
SEA is an evidence-based instrument, aiming to add scientific rigour to PPP making, by using suitable assessment methods and techniques.
From 2005-2007, the effect of the directive was assessed. In 2010, a revised wording was published, integrated with 6 other European directives regulating large industrial sites, into the Industrial Emissions Directive, short IED.